Run SQL queries using phpMyAdmin, Structured Query Language (SQL) is a standardized programming language used for managing relational databases. It allows you to perform various operations such as retrieving data, updating records, and modifying database structures. phpMyAdmin is a web-based tool written in PHP that provides a user-friendly interface for interacting with MySQL and MariaDB databases. Using phpMyAdmin via cPanel makes it convenient to run SQL queries directly on your databases without the need for command-line access.
Step-by-Step Guide to run SQL queries using phpMyAdmin via cPanel
Step 1: Log into cPanel
- Access cPanel: Open your web browser and navigate to your cPanel login page. This is typically
http://yourdomain.com/cpanelor provided by your hosting provider. - Enter Credentials: Log in using your cPanel username and password.

Step 2: Open phpMyAdmin
- Locate phpMyAdmin: Once logged in, scroll down to the Databases section on the cPanel dashboard.
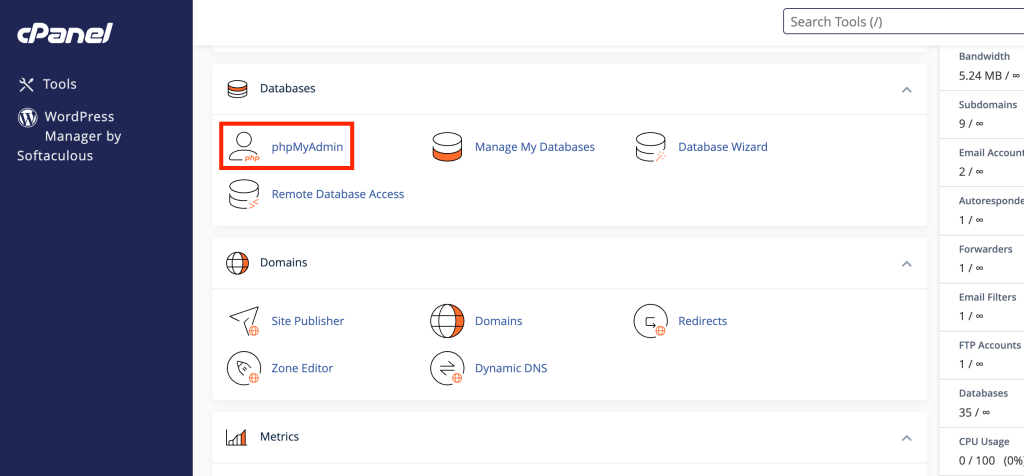
- Access the Tool: Click on the phpMyAdmin icon to launch the application to run SQL queries using phpMyAdmin.
Step 3: Select Your Database
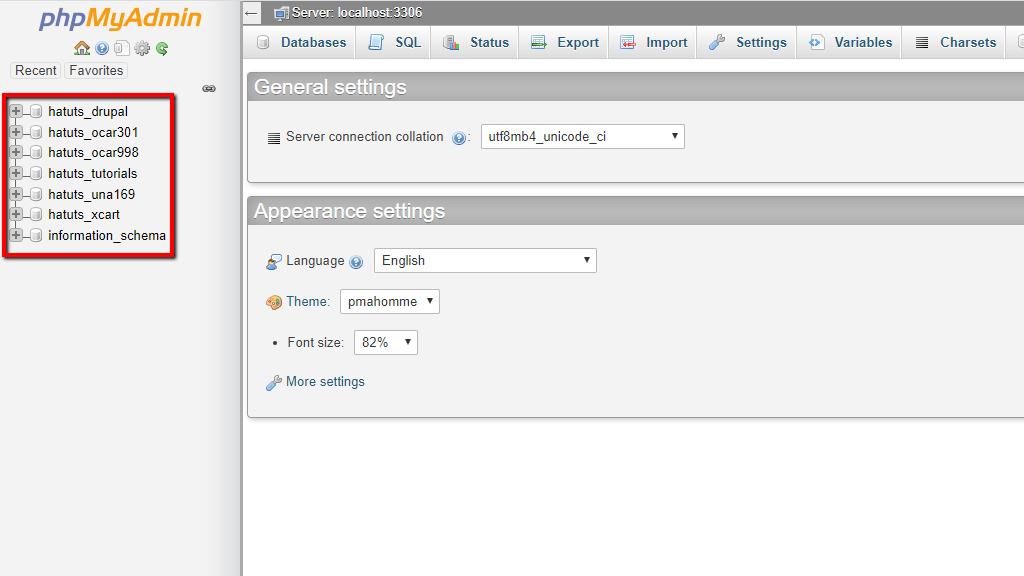
- View Database List: In phpMyAdmin, you’ll see a list of your databases on the left-hand side.
- Choose a Database: Click on the database you wish to run SQL queries using phpMyAdmin. This will display its tables and structure in the main panel.
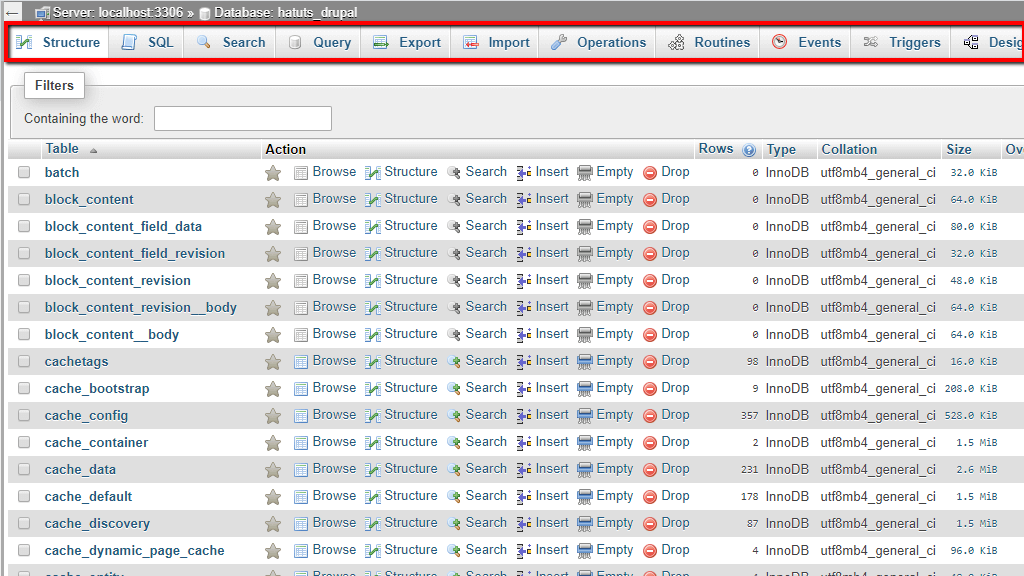
Step 4: Navigate to the SQL Tab
- Access SQL Interface: At the top of the phpMyAdmin interface, you’ll find several tabs like Structure, SQL, Search, etc.
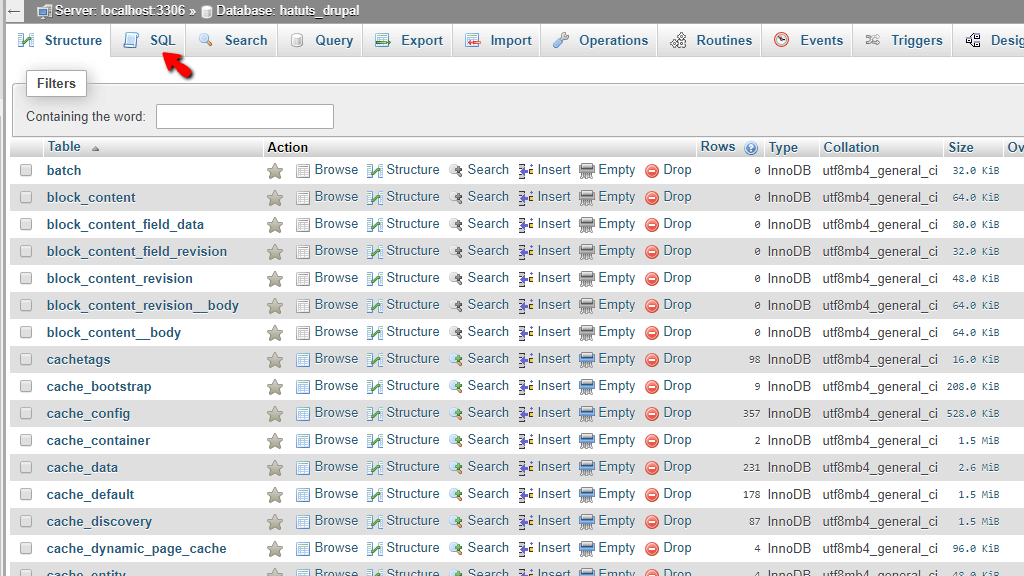
- Open Query Editor: Click on the SQL tab to open the SQL query editor where you can write your commands and run SQL queries using phpMyAdmin
Step 5: Enter and run SQL queries using phpMyAdmin
Type Your Query: In the query editor, enter the SQL statement you want to execute.
For example: SELECT * FROM users;
- Execute the Query: Click the Go button to run SQL queries using phpMyAdmin, typically located at the bottom right of the editor, to run your query.

Step 6: Review the Results
- View Output: After executing the query, phpMyAdmin will display the results below the query editor.
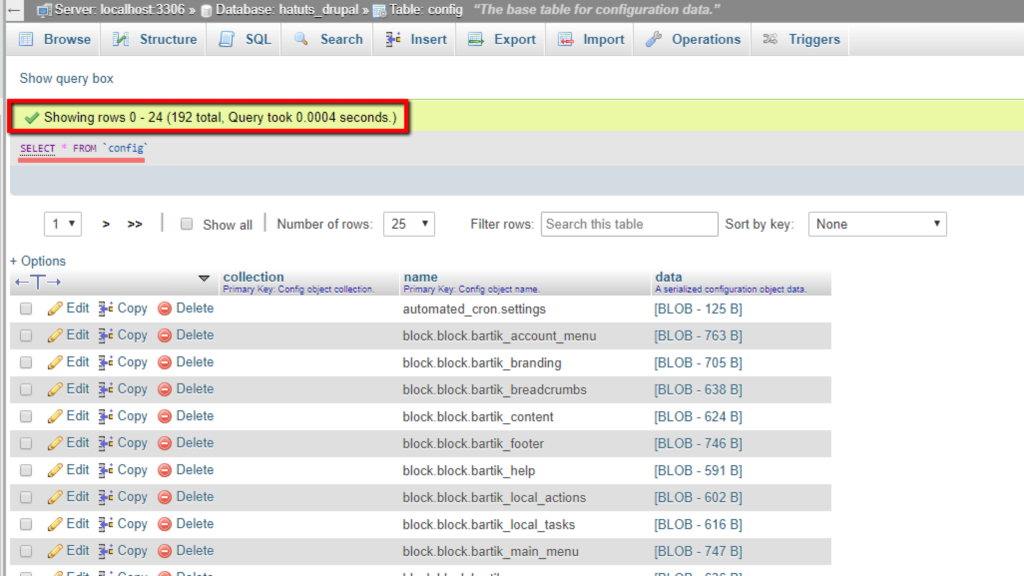
- For SELECT Queries: You’ll see a table with the retrieved data.
- For INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE Queries: You’ll receive a message indicating the number of affected rows.
- Handle Errors: If there’s an error in your query, phpMyAdmin will display an error message with details to help you troubleshoot.
Additional Tips and Examples
- Using Syntax Highlighting: phpMyAdmin’s editor highlights SQL syntax to make it easier to write and read queries.
- Autocomplete Feature: The editor may suggest table and column names as you type, reducing errors.
- Executing Multiple Queries: You can run multiple SQL statements at once by separating them with semicolons (
;).
INSERT INTO users (name, email) VALUES ('Alice', 'alice@example.com');
INSERT INTO users (name, email) VALUES ('Bob', 'bob@example.com');- Common SQL Commands:
- SELECT: Retrieve data from one or more tables.
sql SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name WHERE condition; - INSERT: Add new records to a table.
sql INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2) VALUES (value1, value2); - UPDATE: Modify existing records.
sql UPDATE table_name SET column1 = value1 WHERE condition; - DELETE: Remove records from a table.
sql DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;
Best Practices
- Backup Your Database: Before running queries that alter data, it’s wise to create a backup to prevent accidental data loss.
- Test Queries: If possible, test your SQL statements on a development copy of your database first.
- Use Transactions: For multiple related operations, consider using transactions to maintain data integrity.
START TRANSACTION;
-- Your SQL queries here
COMMIT;- Beware of SQL Injection: Always sanitize inputs if you’re using user-provided data in your queries.
Running SQL queries via phpMyAdmin in cPanel is a straightforward process that empowers you to manage your databases effectively. By following the steps outlined above, you can execute a wide range of SQL commands to interact with your data directly. Always remember to practice caution when running queries that modify data and consider backing up your database regularly.
